Economy
Global Economy Is Gripped by Rare Twin Supply-Demand Shock
Bloomberg05.03.2020Read original
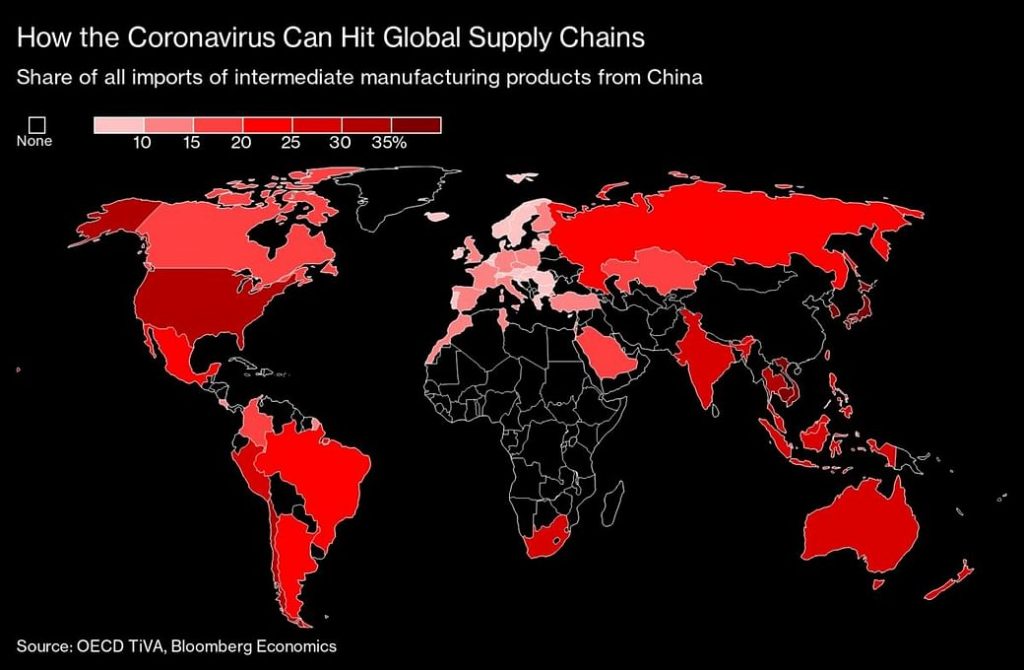
From one side, the epidemic is hammering the capacity to produce goods as swathes of Chinese factories remain shuttered and workers housebound. That’s stopping production of goods there and depriving companies elsewhere of the materials they need for their own businesses.
That supply shock was initially viewed as a short-term disruption, easily reversed once the virus was brought under control. Hence the initial predictions that global growth would follow a V-shaped trajectory, sliding in the first quarter and rebounding in subsequent weeks.
How the Coronavirus Can Hit Global Supply Chains
Those early bets for 2020 are now in tatters because demand is slumping too. With the virus no longer contained to China, increasingly worried consumers everywhere are reluctant to shop, travel or eat out. As a result, companies are likely not only to send workers home, but to cease hiring or investing — worsening the hit to spending.
How the two shocks will reverberate has sparked some debate among economists, with Harvard University Professor Kenneth Rogoff writing this week that a 1970s style supply-shortage-induced inflation jolt can’t be ruled out. Others contend another round of weakening inflation is pending.
The bottom line for central banks and governments is that there’s likely to be even more pressure to deliver economic fixes.
“A classic recession involves a shortfall of demand relative to supply,” David Wilcox, a former Federal Reserve official now at the Peterson Institute for International Economics, said in a report this week. “In that more ordinary situation, economic policy makers know how to help fill in the missing demand. But this case is more complicated because it involves negative hits to both supply and demand.”
Worst Since 2009
The supply-cum-demand blows explain why the world economy is sliding toward its weakest expansion since the 2009 recession, with policy makers’ inflation targets becoming all the more unreachable. Companies including Hyatt Hotels Corp. and United Airlines Holdings Inc. have withdrawn their earnings outlooks, while manufacturers from Samsung Electronics Co. to Toyota Motor Corp. are battling to get production back online.
Those body blows explain why the Federal Reserve’s biggest cut to interest rates since 2008, in an emergency move Tuesday, initially failed to spur the equity market. Rogoff’s warning on product shortages notwithstanding, traders are now pricing inflation over the coming 10 years at just 1.48%, down from 1.80% at the start of 2020, Treasury securities show.
For central banks, the worry is that rate cuts won’t reopen factories or return workers to work. Even to support demand when the virus passes they likely need to be more inventive — combining rate cuts with targeted programs to cushion confidence and keep credit flowing. Another reason for that is most central banks are already short of ammunition after past rate reductions.
With the Fed’s first move flopping, governments are under mounting pressure to do more. In the U.S., the House of Representatives passed a $7.8 billion emergency-spending bill to fund a response to the outbreak — helping deliver a rebound in stocks lacking in the immediate aftermath of the Fed.
“We’re only in the early innings of this crisis,” said former U.S. Treasury Secretary Lawrence Summers.
Slowest Since the Financial Crisis
Some economists argue that what’s happened is mostly a supply side shock, others have highlighted the wallop to demand as well, to the degree that the distinction matters.
Supply shocks are inherently tougher for policy makers to address, because of the difficulty of quickly restoring the production, transport or communication networks or natural-resource inputs affected by the surprise hit.
They most often involve fiscal authorities, who have up to now taken the back seat, leaving central bankers at the wheel. The U.S., Japan, Italy and South Korea are among those that have moved to assemble packages to address the virus, though in most cases they’re tied to the health-care industry and treatment and prevention specifically, not the broader economy.
‘Can’t Help’
“Certainly, rate cuts will not help re-stock emptying grocery shelves,” said Seema Shah, chief strategist at Principal Global Investors. “Monetary policy is hopeless when supply simply cannot feed demand,” she said.
On the demand side, where central bankers are the natural first-responders, the nature of the shock this time can make a broad-brush monetary response less effective. While lower borrowing costs can help give households greater spending power, that aid is limited if millions are shut up at home due to anti-virus measures — or simply because of fears of catching the disease.
Beyond Rates
That may help explain the People’s Bank of China’s preference to use targeted credit measures rather than large-scale interest-rate cuts since the virus erupted early this year. Among their steps, Chinese regulators have let banks run up larger totals of non-performing loans, and loosened guidelines for bond sales.
In Japan, the central bank is likely to consider the introduction of a new lending program to help companies affected by the outbreak of coronavirus this month, according to people familiar with the matter.
The Fed too may need to get more expansive in its moves, Credit Suisse Group AG analysts argue. Zoltan Pozsar and James Sweeney said Tuesday that disruptions to the global supply chain could in turn cause payment failures, tightening financial conditions.
“The supply chain is a payment chain in reverse,” the duo wrote. They urged “open-ended liquidity support through its balance sheet.”
The European Commission is also watching for potential turbulence in the case of a prolonged epidemic. “Cascading effects could stem from liquidity shortages in firms that have to stop production, amplified and spread out by financial markets,” a commission briefing note seen by Bloomberg said.
Global Easing in 2020
Central banks across the world have cut interest rates this year. Last week saw the deepest slide in global equities since the credit crisis, a rapid turnaround from the record high of the MSCI All Country World Index just as recently as Feb. 12. It remains about 8% down on that peak after a 2.7% gain Wednesday, spurred by the U.S. spending move along with relief among some investors that the moderate Democratic candidate for president, Joe Biden, did well in the Super Tuesday primaries. Still, the risk remains of further market disruptions.
“While the Fed’s insurance cuts did serve its purpose into late 2019, the continued lowering of rates may have limited support for markets at present,” said Jingyi Pan, market strategist at IG Asia Pte in Singapore.
It all puts the onus on policy makers to contemplate greater inventiveness. Government spending may not be able to contain the virus spread, but it can help replace free-falling consumer demand. Chetan Ahya, chief economist at Morgan Stanley projects fiscal deficits for the four major advanced economies plus China to rise to at least 4.7% of gross domestic product this year, the most since 2011 and up from 4.1% last year.
“COVID-19 is a particularly pernicious economic shock, as it is both a supply and demand-side shock,” said Mark Zandi, chief economist for Moody’s Analytics.
